EHS regulations and EHS standards exist to ensure organizations in specific industries maintain environmental compliance and workplace safety standards. The purpose of these regulations and standards is to incite behavior that would not otherwise occur and achieve EHS regulatory compliance. By adhering to EHS regulatory compliance requirements, organizations can effectively safeguard the environment and create safe working environments for their employees.
Navigating the Landscape of EHS Standards
EHS standards provide organizations with flexibility in implementing measures that suit their specific operations and circumstances. By adopting EHS standards, organizations mitigate risks and demonstrate their commitment to environmental sustainability and occupational safety.
To navigate the EHS landscape effectively, organizations should stay updated on the latest requirements, assess their applicability, and develop tailored compliance programs. Integrating EHS standards into operations creates a culture of safety, sustainability, and continuous improvement.
The 4 Types of EHS Regulations
According to the Operator Qualification White Paper and Designing Safety Regulations for High-Hazard Industries reports, the 4 types of EHS regulations are:
- Macro-Means
- Macro-Ends
- Micro-Means
- Micro-Ends
The Classification Framework
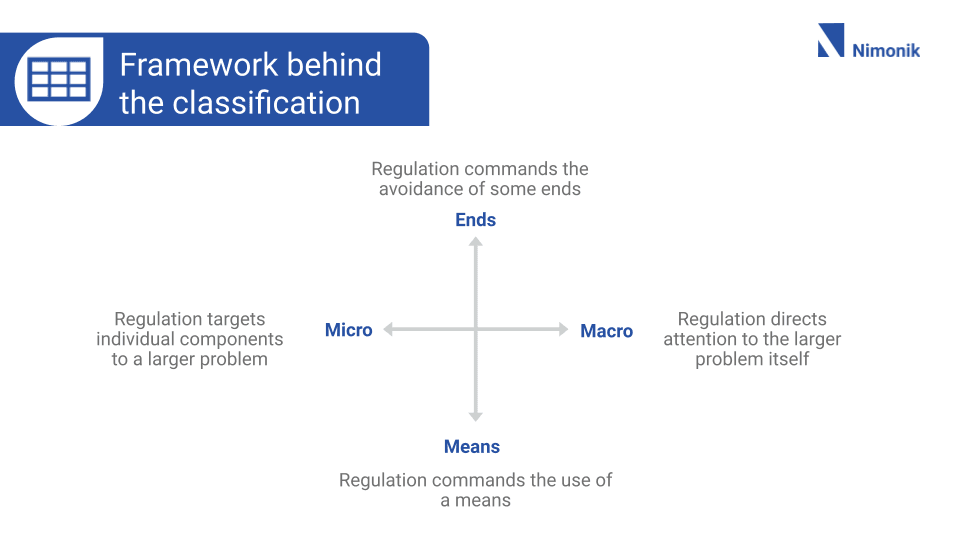
The grid pictured above can help readers understand this classification framework. The “Macro” and “Micro” on the x-axis refers to the specificity of the regulation. Does it target the big picture issue, or smaller components of a problem?
The y-axis, on the other hand, has to do with whether the regulation legislates an “Ends” or a “Means”. Does the regulation command the avoidance of ends such as tailpipe emissions and wastewater emissions, or the use of means, such as documentation processes and valve installations.
Macro-Ends
Examples of Macro-Ends EHS regulations descriptors:
- Tort and ex post liability
- General duty provisions
- Outcome-based regulations
Advantages and Disadvantages of Macro-Ends EHS Regulations
Macro-Ends regulations are the only regulations that focus directly on the ultimate ends. These standards point out the big-picture goals that organizations should be striving toward.
However, this also means that firms may lose sight and underestimate their liability in more non-specific problems. In cases where the harm by non-compliance can be catastrophic, penalty determinations can also be complicated and unacceptable as the exclusive means of regulatory control.
Macro-Means
Examples of Macro-Means EHS regulations descriptors:
- Management-based
- Performance-based
- Goal-based
- System regulation
- Safety case regulation
- Enforced self-regulation
Advantages and Disadvantages of Macro-Means EHS Regulations
Macro-Means regulations are flexible for the regulated entity in operational, technological, and planning. Companies are able to adjust the way in which they want to incorporate these management-based regulations into their daily operations. Macro-Means regulations are also easier for regulators to develop in comparison to the more specific Micro-Means regulations.
However, regulatory agencies typically lack the expertise to review firm-specific management plans, resulting in a lack of quality assurance. Firms may also need to hire personnel with new skills to conduct risk assessment, design, and implement complex management systems.
Micro-Ends
Examples of Micro-Ends EHS regulations descriptors:
- Performance-based
- Output-based
- Market-based
Advantages and Disadvantages of Micro-Ends EHS Regulations
Micro-Ends regulations, due to its focus on results (“Ends”), are closer to the concern. It also allows more flexibility for the regulated industry to adjust their plans according to business processes as long as the ends are achieved.
However, it can be difficult to monitor and track a firm’s attainment of the ends required in Micro-Ends regulations.
Micro-Means
Examples of Micro-Means EHS regulations descriptors:
- Prescriptive regulation
- Design standards
- Technology-based regulation
- Specification standards
Advantages and Disadvantages of Micro-Means EHS Regulations
Micro-Means regulations have very clear instructions for the regulated party, and therefore makes it easier to verify compliance according to such standards. It is relatively simple to take actions in specific problem-areas of an organization’s business process.
However, Micro-Means regulations can also be removed from the ultimate big-picture concerns of the organization. There is also little flexibility for the regulated industry in responding to the regulation.
Empower Your Business with Nimonik
Ensure compliance and elevate your EHS practices with Nimonik. Our comprehensive regulatory and standards tracking software empowers businesses to stay current with evolving requirements and simplify compliance management. Visit our website to learn more and start your journey towards EHS excellence.
FAQs (about EHS Regulations and EHS Standards)
What are the current environmental regulations that EHS regulatory compliance professionals need to be aware of?
The current environmental regulations vary depending on the region and industry. It is important for EHS regulatory compliance professionals to stay updated on the applicable regulations in their jurisdiction. Some common areas of the environment include air quality standards, water pollution controls, hazardous waste management, chemical safety, and workplace safety.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with environmental regulations, and how can EHS regulatory compliance professionals avoid them?
The consequences of non-compliance with environmental regulations are financial penalties, legal liabilities, regulatory enforcement actions such as fines or sanctions, damage to reputation, and potential disruptions to business operations. To avoid these consequences, EHS regulatory compliance professionals should ensure compliance programs in place.
How do environmental regulations differ between states, and what challenges does this pose for ehs regulatory compliance professionals?
Environmental regulations vary by region due to local concerns, resources, and legislation. This poses challenges for EHS professionals and requires a comprehensive understanding of the specific regulations, effective communication across locations, and the ability to adapt compliance programs to meet the unique requirements of each jurisdiction.
What role do EHS regulatory compliance professionals play in ensuring that their organizations are meeting environmental regulations?
EHS regulatory compliance professionals play a crucial role by staying updated on the applicable regulations, interpreting and communicating the requirements to relevant stakeholders, developing and implementing compliance programs, conducting audits and inspections, monitoring compliance status, and addressing any identified non-compliance issues.
What strategies have been effective in helping organizations reduce their environmental footprint and comply with ehs regulations?
Several strategies have proven effective in helping organizations reduce their environmental footprint and comply with EHS regulations. These include:
- Implementing robust environmental management systems
- Adopting sustainable practices
- Engaging employees and raising awareness
- Embracing technology and innovation
- Collaboration and partnerships
Webinar recording
Watch the full webinar recording here- this webinar discusses the meaning and expectations of each of these four types of regulations with concrete examples and best practices on how to comply.







